OXYGEN
ADMINISTRATION
INTRODUCTION
Oxygen
is a basic need and is required to sustain life. The nurse often encounters
clients who are unable to independently meet oxygen needs; the nurse must
understand cardiac and respiratory physiology. Insufficient oxygen and also too much oxygen
supply both are equally harmful for patients. So the nurse who is administering
oxygen should have a through knowledge about the procedure.
DEFINITION
Oxygen
administration is the method of administering oxygen to a patient through a specific device which helps the patient to
gain a normal oxygen saturation in the body.
INDICATIONS OF OXYGEN THERAPY
Ø Obstruction
of air passage.
Ø Bronchial
asthma.
Ø Pneumonia
.
Ø Cardiac
insufficiency.
Ø Peripheral
circulatory failure.
Ø During
operations…etc…
METHODS OF OXYGEN
Ø Oxygen
administration through cannula method.
Ø Oxygen
administration through mask method.
Ø Oxygen
administration through tent method.
OXYGEN ADMINISTRATION THROUGH CANNULA METHOD
It is a method by
which oxygen is administered in low concentration through a cannula which is a
disposable plastic device with two protruding prongs for insertion into the
nostrils.
The purposes are:
·
To
relive dyspnea.
· To
administer low concentration of oxygen to the patients.
· To allow
uninterrupted oxygen supply to patients while eating drinking etc..
SPECIAL PRECUATIONS
·
Never
deliver more than 2-3 ltr of oxygen to patients with chronic lung diseases.
· Check
frequently that both prongs are in patient’s nares.
OXYGEN ADMINISTRATION THROUGH
FACE MASK
Administering
oxygen to the patient by means of ( simple/venturi) according to requirement
of patients.
The purposes are:
·
To
relive dyspnea.
· To
administer higher concentration of oxygen.
SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS
·
The
dosage of oxygen may be ordered as an FiO2 (fraction of inspired oxygen) which
is expressed as liters per minute.
· The
venture mask will have colour-coded inserts that list the flow rate necessary
to obtain the desired percentage of oxygen.
ADMINISTERING OXYGEN THROUGH TENT METHOD
Process of administering oxygen by
means of a tent ,usually for infants which gives maximum comfort and most
satisfactory results.
An oxygen tent consist of a canopy
over the baby’s bed that may cover the baby fully or partially connected to a
supply of oxygen. The canopy’s transparent and helps the nurse to observe sick
baby.
ADVANTAGES
·Provides
an environment for the patient with controlled oxygen concentration,temperature
regulation and humidity control.
· It
allows freedom of movement on bed.
DISADVANTAGES
· It
creates a feeling of isolation.
· It
requires high level of oxygen.
· Loss of
desired concentration occurs every time when the tent is opened to give care
for the infant.
· There is
an increased chance of hazards due to fire .
· It
requires much time and effort to clean and maintain the tent.
SPECIAL
Ø Mist is
prescribed with oxygen therapy to liquefy secretions.
Ø Electrical
equipments used near the tent should be properly grounded.
Ø It is
preferable to monitor the SpO2 of the patient properly.
Ø Avoid
use of volatile inflammable materials near the tent.
Ø For the
baby in the oxygen tent toys selected should be such that they will not produce
static electricity.
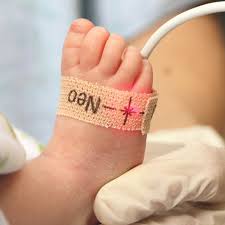
ASSESSMENT OF OXYGEN
SATURATION USING A PULSE OXIMETER
Monitoring the oxygen saturation of
the patient especially who are in oxygen therapy is very essential .
A pulse oximeter is a non invansive
method which has a selected wavelength of light passed to a vascular bed to
estimate arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation. The pulse oximeter uses infrared
light and a process known as spectrophotometer to measure the amount of
oxygenated hemoglobin in arterial blood.
PURPOSE
·
To measure the capillary blood saturation.
·
To detect the presence of hypoxemia before
visible signs develop.
·
To assess the response to therapy.
·
To assess the need to decrease the number of
arterial blood gas specimens drawn.
INDICATIONS
·
Patients who are in oxygen therapy.
·
Patients who experience sudden changes in blood
oxygen level.






No comments:
Post a Comment